Swap nodes in pairs
Swap every two adjacent nodes in a linked list and return its head.
- Created:
- Updated:
- Tags:
- #algorithms #two-pointer #data-structures #linked-list
Problem statement
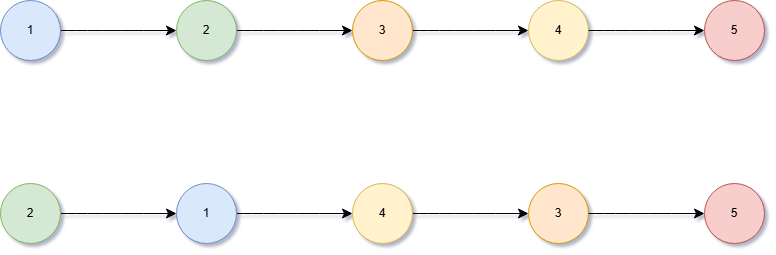
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 100].
- 0 <= Node.val <= 100
Solution
This problem can be solved with the two-pointer tecnhique. We will have two pointers
Step 1
Advance one step the fast pointer
Step 2
Next node to slow will be the next fast node
Step 3
Next node to fast will be the slow node
Step 4
Check if temporal pointer was already set previously.
- If yes: set the previous next node to the fast pointer
- If no: set the new head to the fast pointer so we can return it at the end of the function
Note: in the first step it will just ignore this step.
Step 5
Store in a temporal pointer the slow pointer for next iterations
Step 6
Advance one node the slow pointer
Repeat the steps until slow is null (for linked lists with even number of nodes) OR slow.next is null (for linked lists with with odd number of nodes)
Code
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function swapPairs(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
let newHead: ListNode | null = null;
let slow: ListNode | null = head;
let fast = head;
let previous: ListNode | null = null;
while (slow !== null && slow.next !== null) {
fast = slow.next;
slow.next = fast.next;
fast.next = slow;
if (previous !== null) {
previous.next = fast;
} else {
newHead = fast;
}
previous = slow;
slow = slow.next;
}
return newHead ?? head;
}Complexity analysis
- Time complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the linked list. We traverse the list once, swapping pairs of nodes.
- Space complexity: O(1), we are using only a constant amount of extra space for the pointers.





