Reverse a linked list
Reverse a linked list with the two-pointer technique iteratively.
- Created:
- Updated:
- Tags:
- #algorithms #two-pointer #data-structures #linked-list
Problem statement
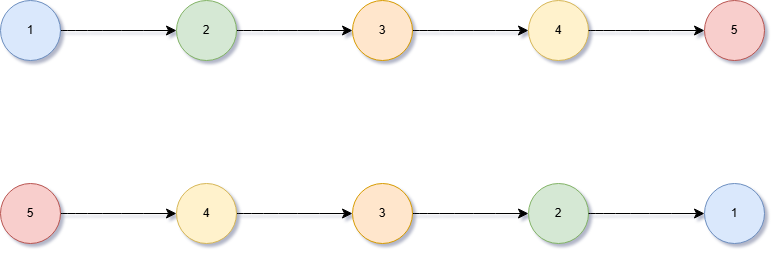
Given the head of a singly linked list, reverse the list, and return the reversed list.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is the range [0, 5000].
- -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
Solution
This problem can be solved iteratively or recursively. The iterative approach is more efficient in terms of space complexity, while the recursive approach is more elegant and easier to understand.
Red is the fast pointer that will be pointing the latest node that will be advanced on each iteration and blue is the slow pointer that will always point to the the head of the linked list.
Having the two pointers at the head of the linked list. If fast is not null and fast.next has a node then:
Step 1
Add a temporal pointer prev that will store slow
Step 2
The slow pointer will be now pointing the next fast node
Step 3
Advance the next fast node to the next node
Step 4
Finally, the slow next node will be the prev pointer
Repeat the steps until fast is null (for linked lists with n = 0) OR fast.next is null (for linked lists with n >= 1)
We can see that the fast pointer is pointing to the last non-null node but there are no more nodes next to the fast pointer.
At the end, return slow as the new head of the reversed linked list.
Code
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
let fast = head;
let slow = head;
while (fast !== null && fast.next !== null) {
let prev = slow;
slow = fast.next;
fast.next = fast.next.next;
slow.next = prev;
}
return slow;
}As simple as that, we have reversed a linked list iteratively with the two-pointer technique.
Complexity analysis
- Time complexity: O(n), where n is the length of the linked list. We traverse the list only once with the fast pointer.
- Space complexity: O(1), as we are using only a constant amount of extra space for the two pointers and one temporal pointer.





